TWO HINGED ARCHES ANDMOMENT DISTRIBUTION METHOD
TWO HINGED ARCHES AND MOMENT DISTRIBUTION METHOD : Two hinged Arches are curved structural members used to support heavy loads on large spans When the load is imposed on an anth it remains primarily under compression. Thus, it receives lower bending moments. As the name indicates, a two hinged arch has hinges only at its supports A two hinged arch has four unknown mactice The number of available equilibrium equations are three. Hence, the degree of static indeterminacy of two hinged arch is equal to 1
ANALYSIS OF TWO HINGED ARCHES
A two-hinged arch loaded with concentrated loads is as shown in the figure below
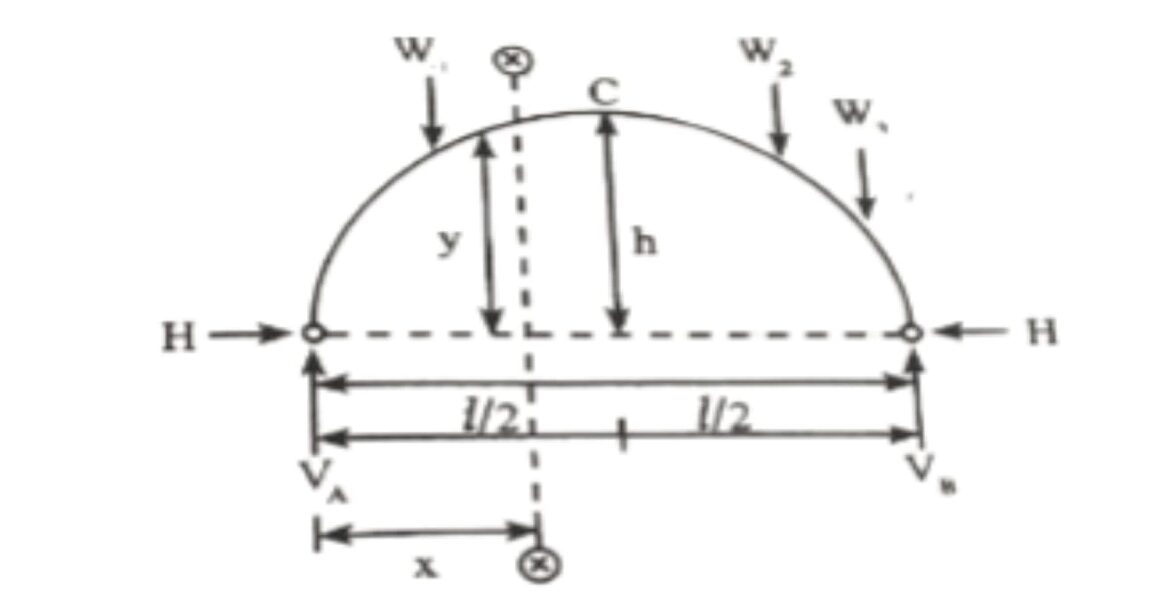
The number of unknown reactions are four and number of available conditions of equilibrium are there. Horizontal thras cannot be evaluated using the available equilibrium conditions. The vertical reactions V and V, can be evaluated by considering moments about any one of the hinges (Le., A or B),
To evaluate the horizontal thrust at each support, Castigliano’s first theorem is used.
A two-hinged arch loaded with Uniformly distribution loads is as shown in the figure below
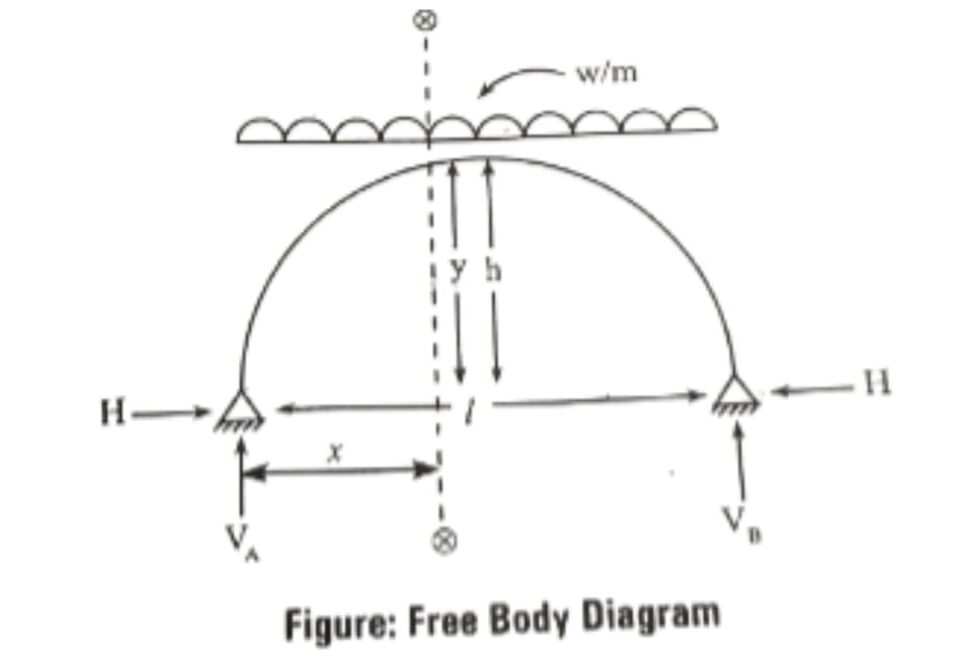
A two hinged parabolic arch of length ” and rise ‘h’ which is loaded with U.D.L of w/m intensity is as shown in the figure below. It experiences only horizontal thrust which coincides with the arch profile and the effect of the bending moment and shear force at any section of the arch is zero.
MOMENT DISTRIBUTION METHOD
Moment distribution method suggested by Profestor Handy Cross is mostly adopted to analyse the statically indeterminate beams and frames
In this method, fixed end moments are evaluated by assuming that each und every joint of structure is fixed In this stages, joint moments are unbalanced. Therefore, in order to change the unbalanced moments to balanced moments fixity at the joint is released and the rotation is permitted, until the joint moments are balanced. In other words, balancing moments. which is equal and opposite to the unbalancing moment, is applied at the joint.
ANALYSIS OF MOMENT DISTRIBUTION METHOD
The following steps are to be followed for analysing a portal frame with inclined legs.
(1) The fixed end moments for different spans of the frame are calculated
(ii)The distribution factors at intermediate joints and their connecting members are determined.
Distribution factor, D. F = k/(Sigma*k)
Where,
k – Individual stiffness of member at a joint
Sigma*k – Total stiffness of all members meeting at joint
iii) The non-sway moment distribution due to the external forces is carried out and final moments obtained are noted.
(iv) The restrained joint is released and the force acting at that joint is calculated using the geometry and the boundary conditions
(v) Assuming an arbitrary sway (say ‘8’) in any member, the sway in other members is calculated in terms of “8”.
(vi) The fixed end moments in all the members are calculated for different joints
(vii) The sway moment distribution process is carried out for the moments obtained in above step
(viii) The sway force acting on the frame due to the moments obtained in (vii) is calculated.
(ix) Correction factor (ratio of restraining force to arbitrary sway force) for the frame is computed.
(x) The arbitrary sway moments are corrected using the correction factor and actual sway moments are determined.
(xi) The final moments are finally calculated by adding the non-sway moments to the actual sway moments.
(xii) The shear force and bending moment diagram of the frame are drawn
