MEASUREMENT OF LIQUID PRESSURE
MEASUREMENT of LIQUID PRESSURE various devices used for measuring liquid pressure may be classified as,
(a) Manometers
(b) Mechanical gauges.
(a) MANOMETERS
Manometers are further classified as.
1. Simple Manometers
2. Differential Manometers
Simple Manometers measure pressure at a point in the liquid contained in a pipe or vessel. Differential manometers measure the pressure difference between two points in a liquid.
1.Simple Manometers
Three types of simple manometers exist.
1. Piezometer
2. ‘U’ Tube Manometer
3. Single Column Manometer.
1. Piezometer: A piezometer is a glass tube inserted in the wall of pipe or a vessel for the purpose of measuring the pressure. The pressure at any point in the liquid is indicated by the height of liquid level in the tube above that point. Thus, if wis specific weight of liquid, then pressure at ‘A is p = wh. Piezometers are used to measure gauge pressure or static. It cannot be used to measure large pressures in lighter liquids and also gas pressures.
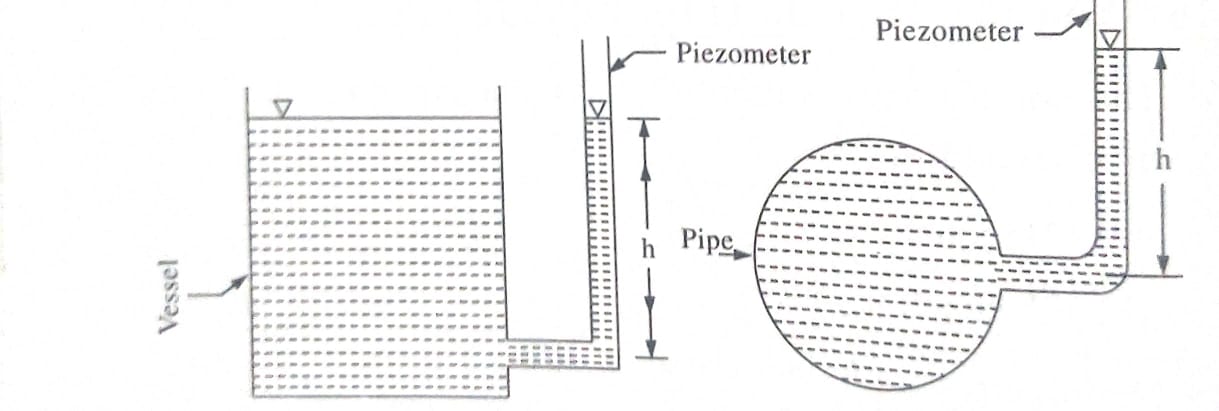
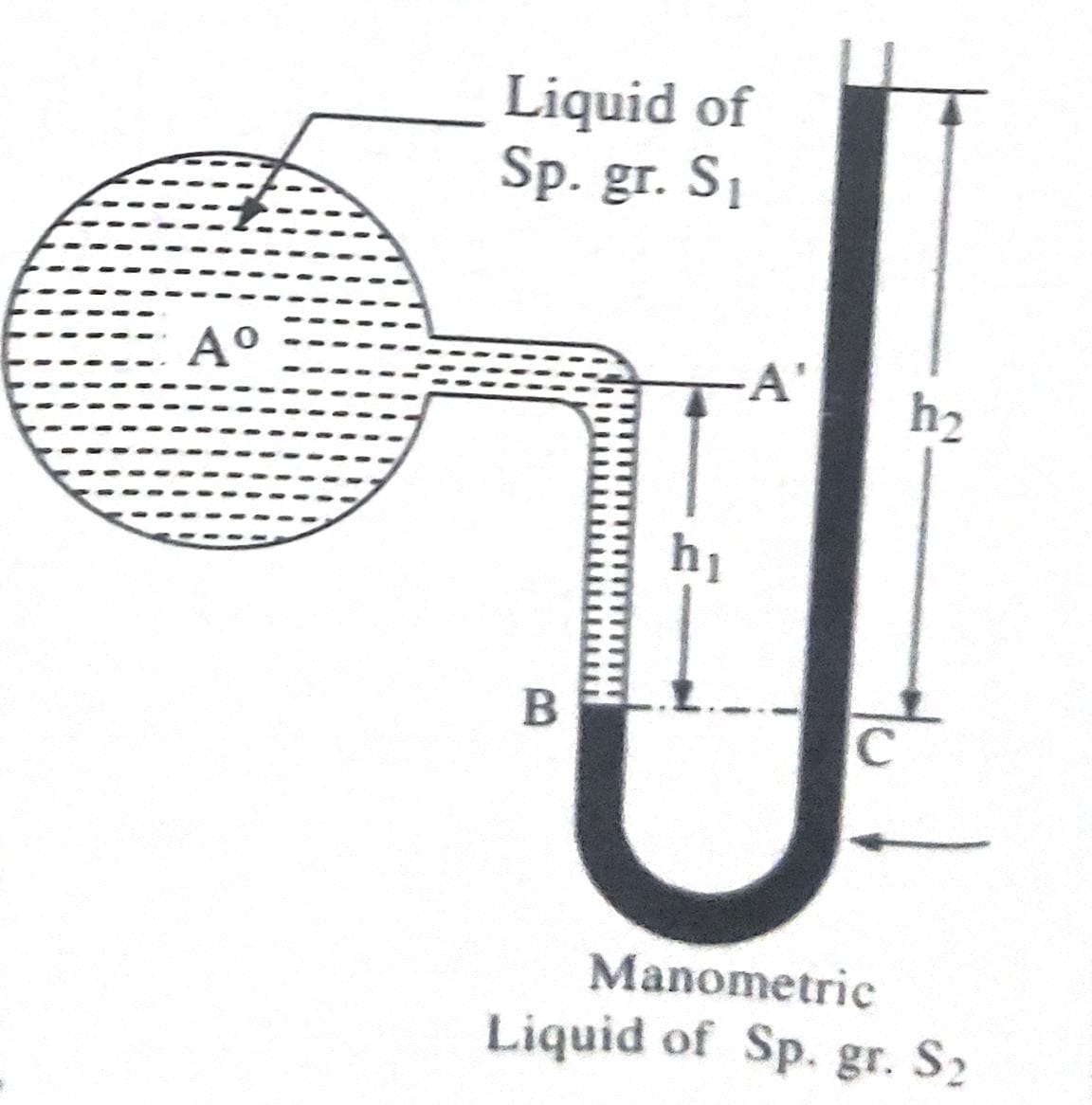
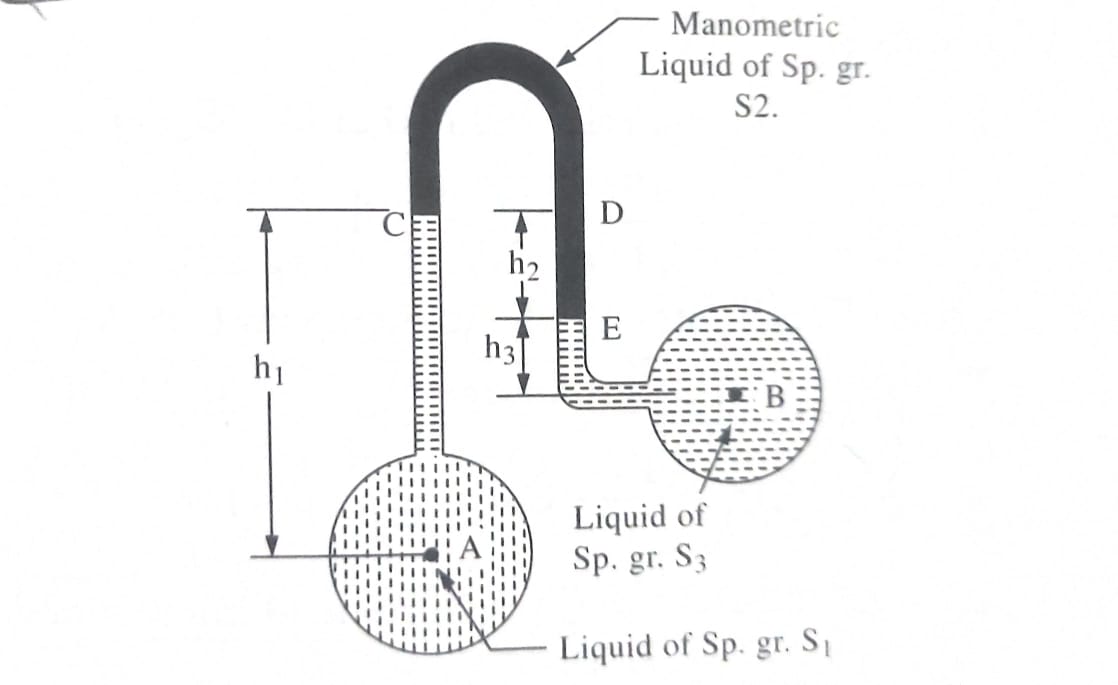
2.U’ Tube Manometer: U Tube manometer is an U- shape glass tube whose one end is connected to gauge point and other end remains open to atmosphere. Tube contains a manometric liquid of specific gravity greater than that of liquid of which pressure is to be determined. It is also used for measuring negative pressures.
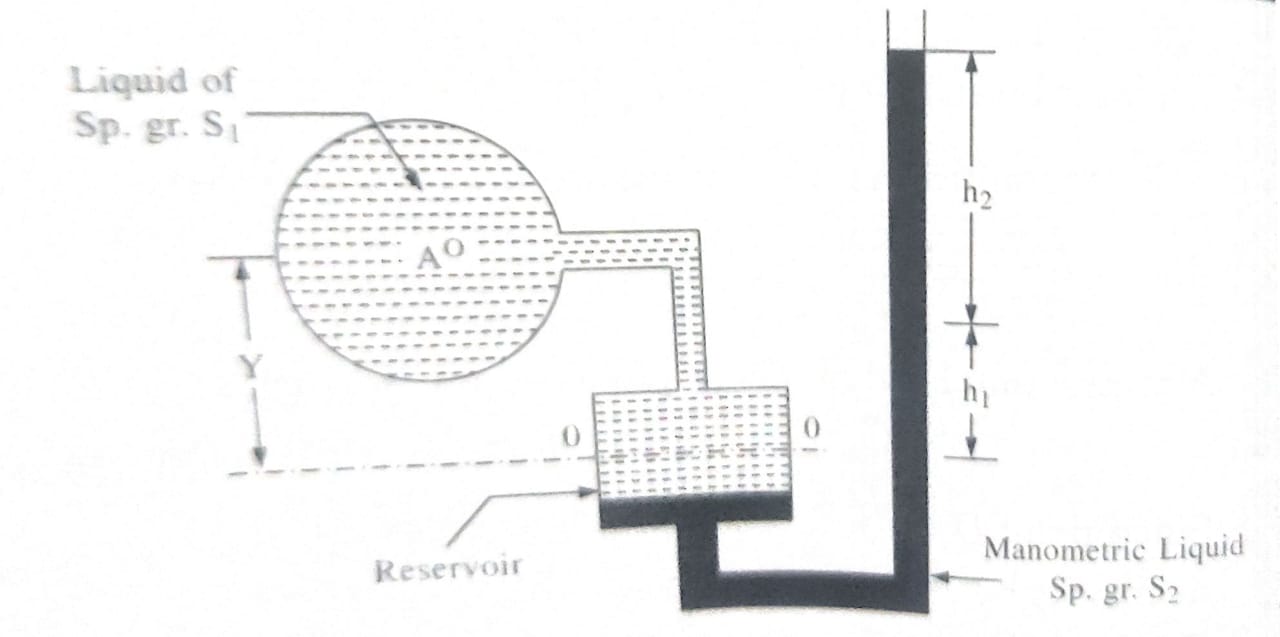
3.Single Column Manometer:The U-tube manometer usually require readings of liquid levels at two or more points. This difficulty may be overcome by using single column manometers. In single column manometer a reservoir of targe cross sectional area is fitted in one leg of manometer as shown is the manometric liquid level before the manometer is connected to pipe. Due to pressure of liquid column of height y, manometric liquid rises to a height of h_{1} in open leg.
y×S1=h1×S2
If manometer is connected to gauge point, manometric liquid level rises to a height of h₂ due to liquid pressure. So, by measuring total rise of manometric liquid level (h₁ + h₂) in open leg we will determine the pressure at gauge point from the equation. P/w=h₂ [S2+(S2-S1) a/A] Where A and a are cross-sectional areas of reservoir and tube respectively.
2.Differential Manometers
For measuring the pressure difference between two points a differential manometer is used. It consists of a bent glass tube, whose two ends are connected to two gauge points. they are four types of differential manometers are,
1. Two-Piezometer Manometer
2. Inverted U-Tube Manometer
3. U-Tube Differential Manometer
4. Micromanometer
1. Two – Piezometer Manometer: It consists of two separate piezometer which are connected to two gauge points. The difference of the liquid levels in two piezometers will give pressure difference between gauge points.
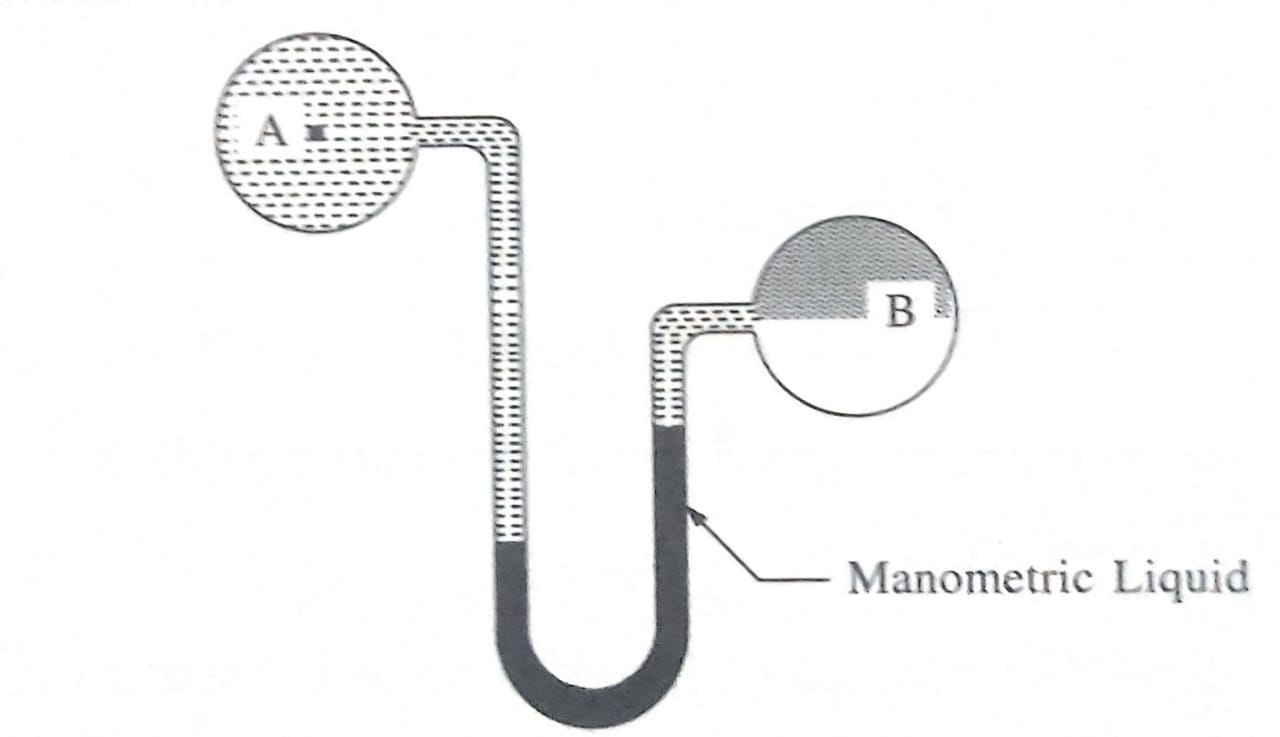
2. Inverted U-Tube Manometer: It consist of U-shape glass tube which is held inverted whose two ends are connected to two gauge points. It is suitable for measurement of small pressure difference in liquids. In this type of manomyeter lighter manometric liquid is used.When inverted U-tube manometer is connected to two gauge points, manometric liquid move upwards in one limb and falls in another limb as shown
3.U Tube Differential Manometer: AU-Tube differential manometer is an U-shape glass tube whose ends are connected to the two gauge points between which pressure difference is to be measured. Lower part of manometer contains manometric liquid which is heavier than liquid for which pressure difference is to be measured. In order to determine pressure difference between two gauge points, gauge equation should be developed same as that of inverted differential manometer.
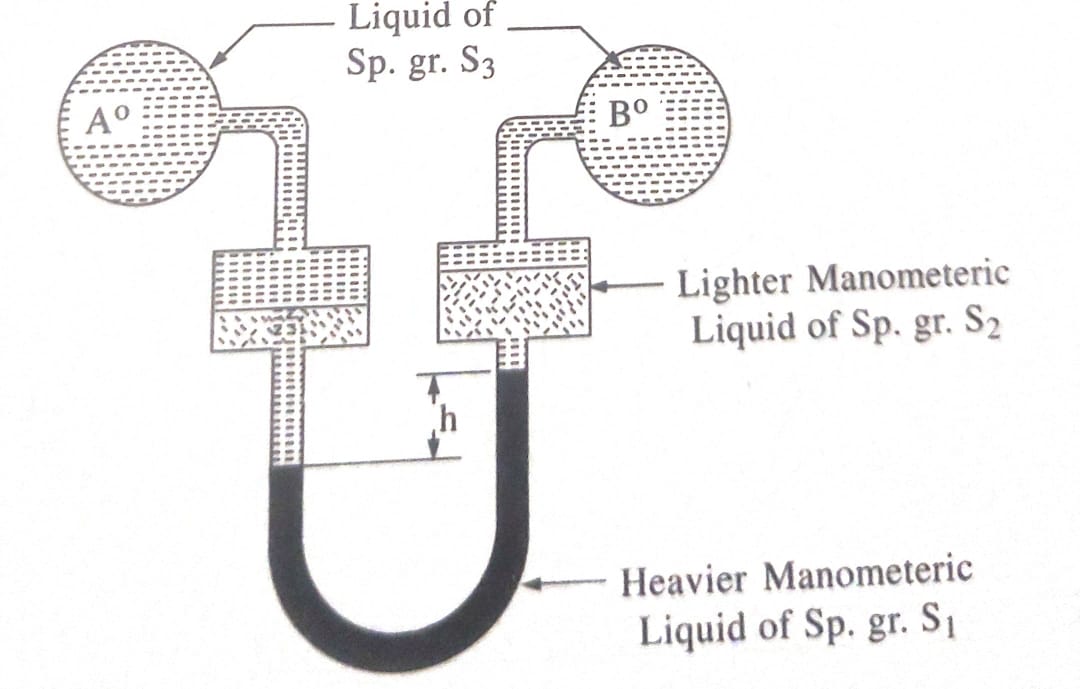
4.Micromanometer: It consists of a glass u-tube, provided with two reservoirs of wider sections at the top of two legs . In this manometer two manometric liquids of different specific gravities are used. For measuring very small pressure difference or for measuring pressure difference with high precision micromanometers are used.
(b)Mechanical Gauges
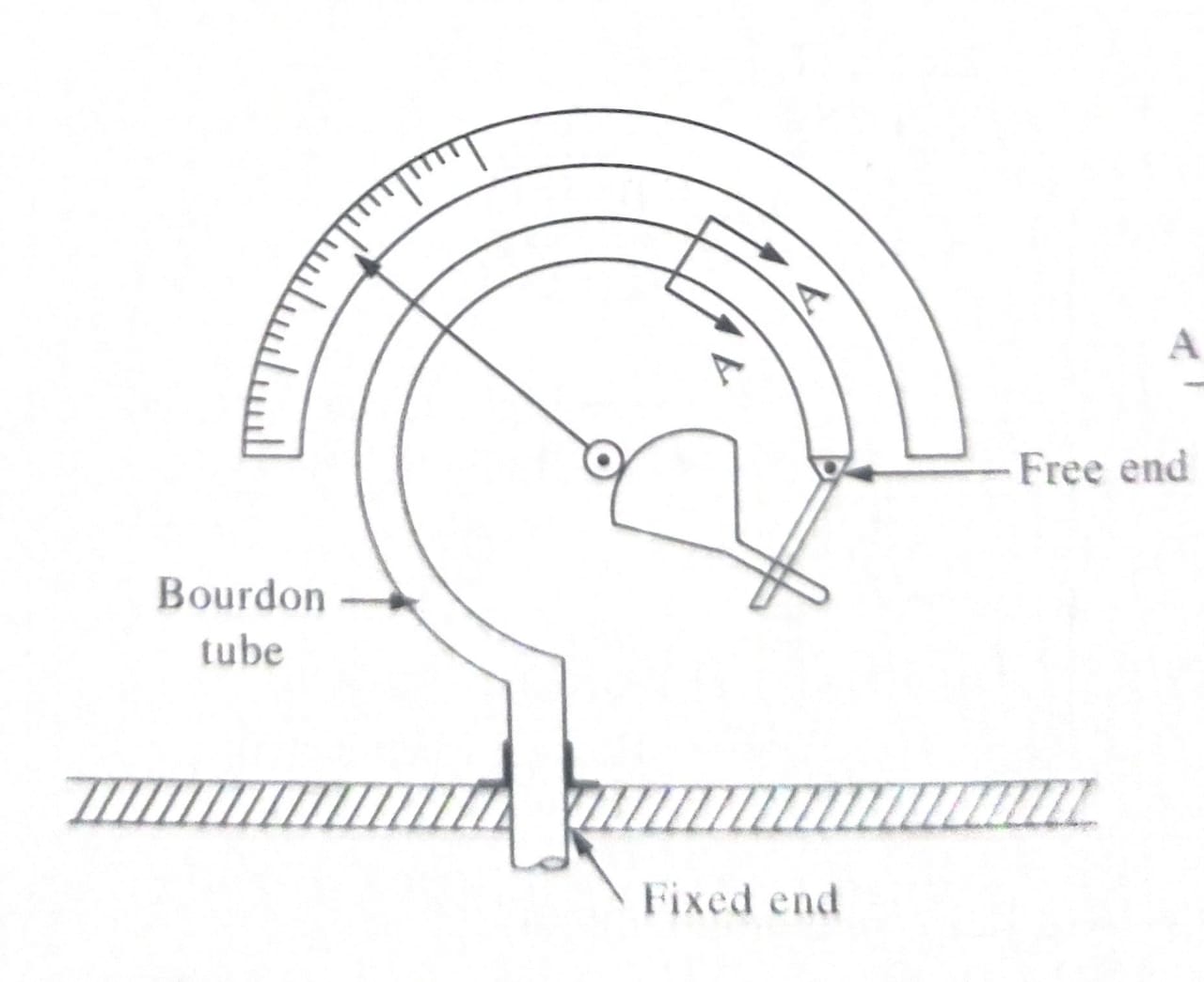
Mechanical gauges measure high pressures and are used where high precision is not necessary. Among several types of mechanical gauges, the Bourdon tube pressure gauge is widely used to measure gauge pressures. This consist of a steel or bronze tube of elliptical cross section, bent in the form of circular arc. The tube is closed at outer end and this end of tube is free to move. The other end of tube is rigidly fixed to the frame, which is connected to gauge point. When the gauge is connected to the gauge point, liquid under pressure enters the tube. This pressure tends to straighten the tube. This movement is transmitted by lever arrangement and causes the pointer to rotate over the graduated circular dial which indicates the pressure intensity of the liquid.