FLOW THROUGH ORIFICE AND MOUTHPIECES
Flow through orifice and mouthpiece Users measure the rate of flow of liquid using both the orifices and mouthpieces.
ORIFICE

An orifice is a small opening of any cross section (such as Fe circular, square, triangular, rectangular etc.) made in the walls or the bottom of a tank containing liquid, through which liquid me is flowing.
CLASSIFICATION OF ORIFICES
The orifices are classified on the basis of their size, shape shape of upstream edges and the discharge Following are the important classifications:
1.According to the size, the orifices are classified as small orifice and large orifice. If the head of liquid from the centre of orifice exceeds five times the depth of the orifice, it is termed as a small orifice. If the head of the liquid is less than five times the depth of the orifice, it is termed as a large orifice.
2 According to the shape, the orifices are classified as circular, rectangular, square and triangular. Out of these circular and rectangular orifices are widely used.
3 According to the shape of upstream edge, the orifices are classified as sharp edged orifices and Bell – mouthed orifices
4. Depending upon the nature of discharge, the orifices are classified as free discharging orifices and submerged or drowned orifices. If the jet of liquid coming out of the orifice falls freely in the atmosphere it is known as free discharging orifice. If the liquid level on the downstream side of the orifice is above the top edge of orifice, it is called as fully submerged orifice. If the liquid level on the downstream side is between the bottom and top edge of the orifice it is known as partially submerged orifice.
MOUTHPIECE
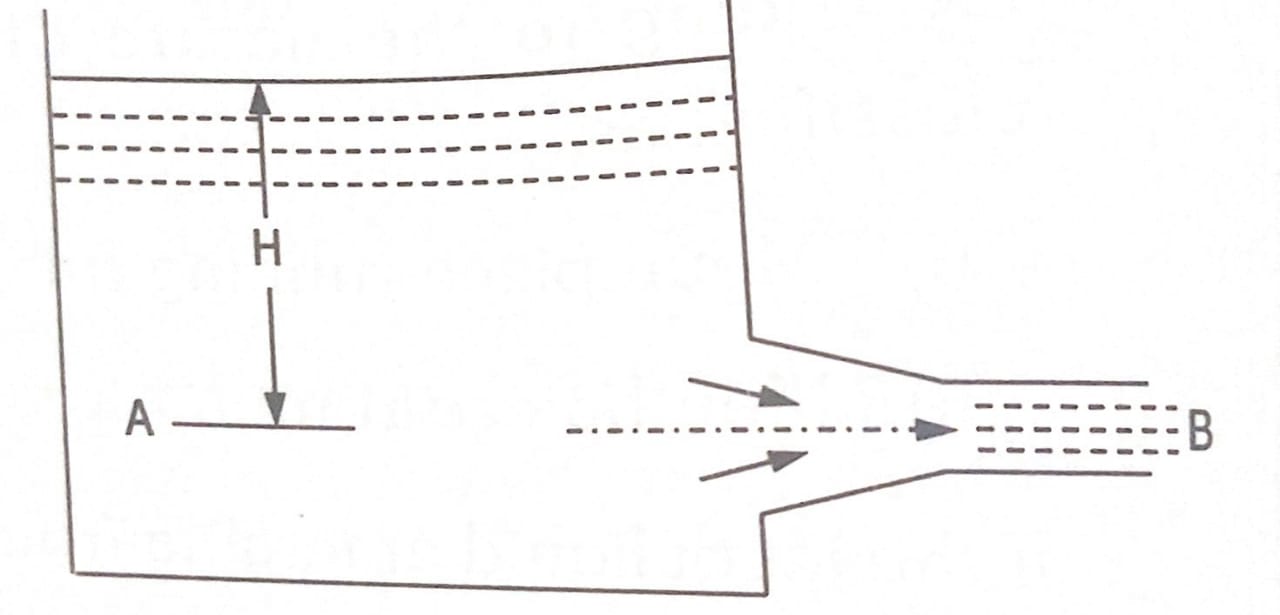
A mouthpiece is a short length of a pipe which is not more than two to three times its diameter, fitted to an orifice of same diameter, provided in a tank containing liquid
CLASSIFICATION OF MOUTHPIECE
The mouthpieces are classified on the basis of their shape position and nature of discharge.
According to the shape, the mouthpieces are classified as
1 Cylindrical Mouthpiece
2.Convergent Mouthpiece
3.Divergent Mouthpiece and
4.Convergent – Divergent Mouthpiece
According to the position, mouthpieces are classified into two types
1 External mouthpiece and
2.Internal mouthpiece
When the tube is fixed externally to the orifice, it is known as external mouthpiece. If the tube is projects inside the tank, it is called an internal mouthpiece
According to the nature of discharge, mouthpieces are classified as,
1.Mouthpiece running full and
2.Mouthpiece running free
The jet of liquid emerging from the mouthpiece is said to be running full if it is of the same diameter as that of the mouthpiece. The jet is said to be running free if it does not touch the sides of the mouthpiece.
