Flexibility Matrix Method for analysis of structure
Flexibility matrix method is originated by the systematic development of the consistent deformation method in the matrix form. The redundant forces are the basic unknowns in this method. Degree of static indeterminacy represents the number of redundant forces. The consistency conditions are developed by determining the displacements which are developed in the basic determinase structure as a result of the given loading. The equations formed are to be solved in order to evaluate the redundant forces. Then, the desired quantities at any section can be evaluated. The equations which are formed will be in the form of matrix This method is also known as force or compatibility method.
1.Flexibility Method It is a systematic development of consistent deformation method of structural analysis.
2. In this method, the basic unknowns are forces (either reaction or moments).
3. Degree of static indeterminacy is required to find the number of co-ordinates.
4.Consistency or compatability conditions are formed for analysis.
5. An element (say delta_{alpha} ) represents the displacement at co-ordinate ‘i’ due to the application unit force at co-ordinate ‘j’.
6.Flexibility matrix has diagonal symmetry i.e., delta ij = delta ii .
7. The forces in the members of beam or structure are evaluated using the statics.
8. Flexibility method cannot be transferred easily into a computer program.
9.More computational effort (i.e, more calculations) and more time is required to develop flexibility matrix when compared to stiffness method.
The steps to be followed to obtain the solution by flexibility method are
1.The degree of static indeterminacy ‘n’ is to be determined initially
2 The redundants are Flexibilityto be selected.
3.The coordinates are assigried to the redundant force directions
4.Restraints to the redundant forces are removed to obtain the basic determinate structure.
5.The deflections developed in the coordinate directions as a result of the given condition of loading are evaluated.
6. The flexibility matrix is to be determined.
7 The compatibility condition to be applied is,
8.The forces in the members of structure are evaluated after determining the redundant forces.
Steps Involved in Flexibility Method
1.Initially, the degree of static indeterminacy of the structure is to be determined. By releasing (ie, removing) the redundant forces (Number of releases is equal to the degree of static indeterminacy), the structure is made statically determinate.
2 Indeterminacy can either be external, internal or both.
3.Releases should be selected in such a way that the structure is statically determinate, stable and suitable to find displacements On the released coordinates.
4.Calculate the displacements of the primary structure, by finding all the redundants released in the direction of releases
5. Any standard method involving translations, rotations or both can be used to find displacements. These displacements form a displacement vector [A,).
6 Displacements are determined at the released coordinates by applying unit load at all coordinates.
7.To determine final forces in the structure, external loading and redundant forces should be superimposed on released structure
fiexibility matrix method for analyzing statically indeterminate structures.
Flexibility is defined as the displacement caused at a joint due to the application of unit force, while maintaining all other diplacements as constant. It is generally denoted by
th analysing an andetectsiste structure using flexibility method, the main requirement is to develop a flexibility mater For this purpose, kondy and applied at the required positions and the displacement due to these loads are calculated first. The int and the direction of required displacements. The loads are applied successively at different coordinates and the displacements at other coordinates se calculated for each load. The relationship between the displacement at coordinate flexibility and the applied forces in matrix form is given by.
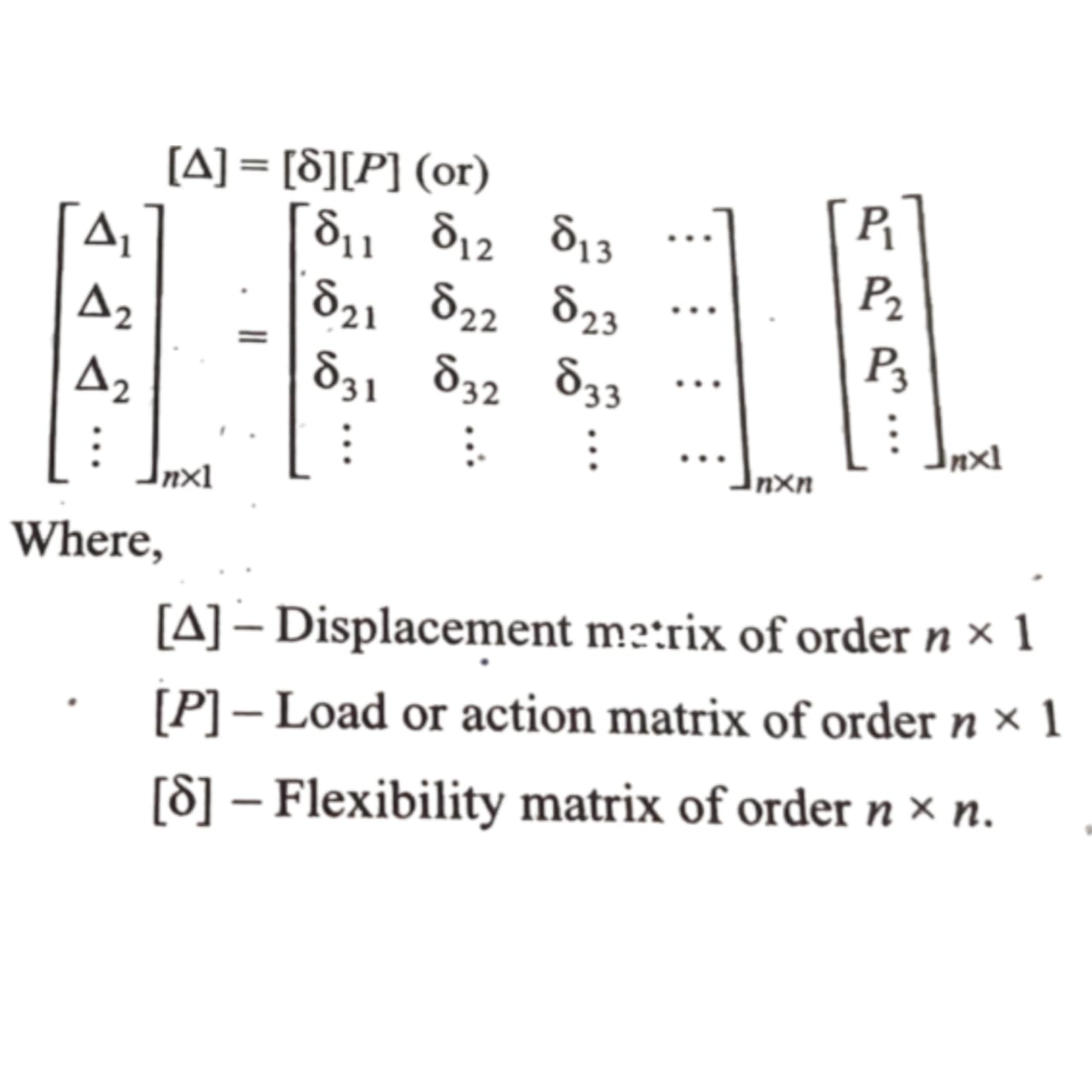
The flexibility &, represents the displacement caused at the coordinate ‘i’ due to application of unit load at coordinate The principal diagonal elements of a flexibility matrix (where i) are known as direct flexibility coefficients and they represes the forces and displacement at the same corresponding coordinates.
The remaining elements except the principal diagonal elements are known as cross flexibility coefficients and represen the displacement caused at a coordinate due to force applied at any other coordinate
